Geotheta Fundamentals Explained
Geotheta Fundamentals Explained
Blog Article
The 15-Second Trick For Geotheta
Table of Contents8 Simple Techniques For GeothetaThe 10-Minute Rule for GeothetaGetting The Geotheta To WorkThe Geotheta Diaries
They team up with civil designers, structural engineers, architects, and various other experts to incorporate geotechnical factors to consider right into the total job style and building and construction procedure. This calls for efficient teamwork, control, and interaction to ensure that the geotechnical aspects straighten with the project purposes and fulfill regulatory requirements.Mining & Products Engineering: Principles of boring, penetration rates, and aspects affecting the choice of drilling approach. Blowing up techniques in surface and underground operations. Mechanical and continuous strategies to fragmentation, including longwall shearing and fullface boring.
Modelling of piece and bit dimension circulations; comminution as a transfer feature. Comminution innovation: crushing, grinding, dimension category. Integrated analysis of fragmentation and comminution operations. Supplied by: Mining & Materials Engineering.
Geotheta Can Be Fun For Anyone
Bachelor's degree programs in civil, geotechnical, geological, and ecological design generally last 4 years and consist of general education training courses in English, social science, and the liberal arts, along with courses in sophisticated maths, structural geology, and liquid mineralogy. (https://www.openstreetmap.org/user/geotheta)
Geotechnical engineering includes the assessment of the dirt and rock conditions at a particular website, and their ramifications for the advancement of that site. As a lot of structures rely upon the ground for support, it lacks shock that a thorough understanding of the ground problems, and the suitability of structure systems, are vital to the long-term security and efficiency of the building or framework.
Specialising in the examination of geological formations and ground practices, geotechnical designers perform clinical investigations and testing to recognize the impact these geological formations may have on the layout and building of structure, civil and infrastructure jobs. This knowledge is vital for the design and construction of buildings, roadways, tunnels, dams, bridges, and water and sewer systems.
The geotechnical group at Douglas Partners routinely speak with designers, style engineers, designers, and home builders to make recommendations on layout and advancement proposals to ensure that the developed structures are suitably developed for the ground problems. The layout of footing systems needs to consider the weight of the structure, the capacity of the ground to sustain that weight with each other with motion resistances and effective building and construction.
Indicators on Geotheta You Should Know
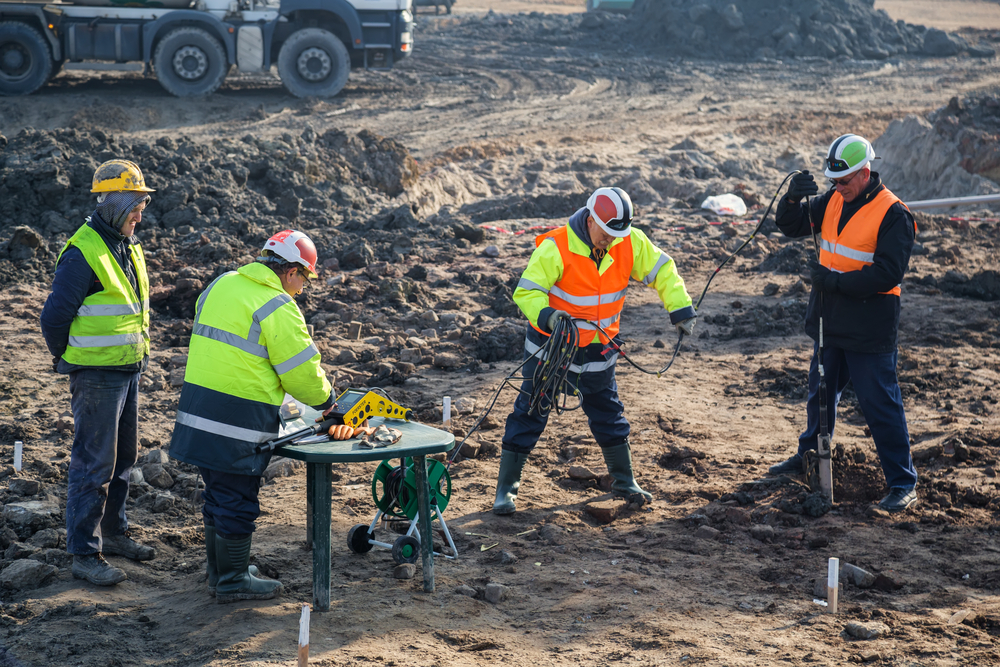
This task is substantially simplified by the use of our Douglas Map geospatial system that makes this info readily easily accessible in a simple to make use of internet browser user interface. A geotechnical engineer will direct the boring of boreholes and examination pits to gather dirt and other samples, and additionally evaluate surface area features and ground exposures to create a geotechnical design of the subsurface problems.
Depending upon the project type and ground problems experienced, lab testing may among various other things examine strength, compressibility, reactivity and/or permeability of dirt and rock examples. Hereafter information is accumulated and collected, the outcomes are used for a geotechnical model of the site, which is generally offered as sections throughout the website.
A geotechnical investigation naturally can only examine the ground conditions at the places pierced or dug deep into. Natural variations in dirt and rock problems can happen throughout a website and in between test areas. It is for that reason excellent practice that the geotechnical designer be maintained throughout building and construction of the task to give on-site confirmation that the ground conditions run into follow the expectations and recommendations given in the geotechnical investigation report.
The 3-Minute Rule for Geotheta
Geotechnical designers utilize their thorough expertise of dirt and rock to examine risk and solve issues on diverse framework projectsGeotechnical engineering is a specialist branch of civil design which looks at the behavior of planet materials and the application of soil and rock technicians. Geo Tech Engineer. As a geotechnical engineer, you will certainly analyze the physical, mechanical and chemical residential or commercial properties of soil and rock in order to develop foundations, retaining structures and earthworks
Geotechnical design is carefully linked to and overlaps with, both design geology and ground engineering - https://moz.com/community/q/user/geotheta?_gl=1*xkyvtd*_up*MQ..*_ga*NjU0Mjk2NzIxLjE3MjI2MDU1Nzc.*_ga_DS7K9Q3S5W*MTcyMjYwNTU3Ni4xLjAuMTcyMjYwNTU3Ni4wLjAuMA... It's possible to specialise in geotechnics or work for a geotechnical company however be called a design geologist or a ground engineer. As a geotechnical designer, you'll need to: construct and keep partnerships with customers and other specialists involved in the site, throughout each projectmaintain safety and security standards on site bear in mind price implications when you make recommendationsstudy geological maps and aerial photos from a variety of sources and from different time periodsexamine building and construction plans to see how feasible they are based upon your understanding of the siteinvestigate risks or geological dangers for the sitesearch for eco sensitive features, such as garbage dump begin to create accurate and interpretive ground modelsplan field investigationsdrill and evaluate examples of bedrock, dirt, groundwater and additional materials monitor other professionals on sitesolve technological problems as they emerge, such as unexpected structures at drill sitesmonitor problems during and after construction to see to it frameworks are stable in the brief and long termadding information collected on site to your first researchcreating geotechnical computations, illustrations, and 2 or three-dimensional computer designs translating the datamaking suggestions about the suggested use the website

Report this page